Key concepts
Enterprise architecture portfolio meta model
Enterprise Architecture Portfolio Model Concepts
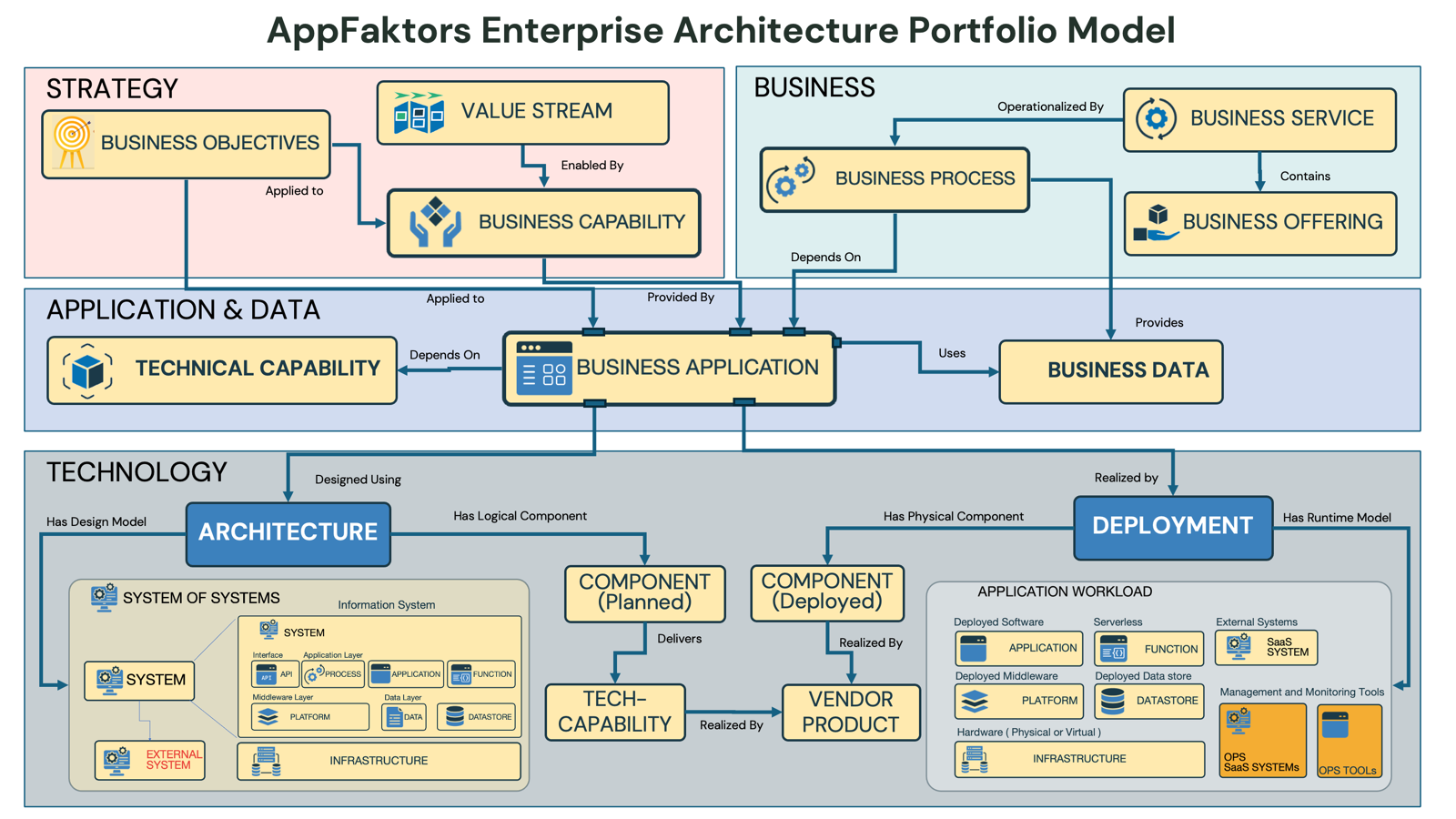
Overview
The AppFaktors Enterprise Architecture Portfolio Model provides a comprehensive framework for organizing and managing enterprise architecture artifacts across four key layers: Strategy, Business, Application & Data, and Technology. This model ensures alignment between business objectives and technology implementation while maintaining clear relationships and dependencies across all architectural domains.
Model Architecture
Four-Layer Framework
The model is structured as a vertical stack with clear relationships and dependencies:
- Strategy Layer (Top) - Strategic direction and objectives
- Business Layer - Business processes and services
- Application & Data Layer - Applications and information assets
- Technology Layer (Bottom) - Technical infrastructure and deployment
Layer Descriptions
1. Strategy Layer
Purpose: Defines the strategic direction and business objectives that drive architectural decisions.
Components
Business Objectives
- Definition: High-level organizational goals and strategic priorities
- Role: Provides strategic direction for all architectural decisions
- Relationship: "Applied to" Value Streams to ensure strategic alignment
Value Stream
- Definition: End-to-end series of activities that deliver value to customers
- Role: Translates business objectives into operational capabilities
- Relationship: "Enabled by" Business Capabilities
Key Relationships
- Business Objectives → Value Stream: Strategic goals are applied to value creation processes
- Value Stream → Business Capability: Value delivery is enabled by specific business capabilities
2. Business Layer
Purpose: Represents the business architecture including processes, services, and operational structure.
Components
Business Process
- Definition: Structured activities and workflows that accomplish business objectives
- Role: Operational implementation of business capabilities
- Relationship: "Operationalized by" Business Services
Business Service
- Definition: Discrete business functions that support business processes
- Role: Modular business functionality that can be composed and reused
- Relationship: "Contains" Business Offerings
Business Offering
- Definition: Products or services delivered to customers or stakeholders
- Role: Value delivery mechanism to end customers
- Relationship: "Provides" Business Data
Key Relationships
- Business Process ↔ Business Service: Processes are operationalized by services
- Business Service → Business Offering: Services contain specific offerings
- Business Capability → Business Process: Capabilities depend on processes for execution
3. Application & Data Layer
Purpose: Manages application portfolio and information architecture supporting business operations.
Components
Technical Capability
- Definition: Reusable technical functions that support business operations
- Role: Bridge between business requirements and technical implementation
- Relationship: "Depends on" Business Applications for implementation
Business Application
- Definition: Software systems that support business processes and capabilities
- Role: Central orchestrator of technical capabilities and data
- Relationships:
- "Applied to" from Business Capabilities
- "Provided by" to Business Capabilities
- "Uses" Business Data
Business Data
- Definition: Information assets and data structures used by applications
- Role: Information foundation supporting business operations
- Relationship: "Provides" data to the Business layer
Key Relationships
- Business Capability ↔ Business Application: Bidirectional support relationship
- Business Application → Business Data: Applications use and manage data
- Technical Capability ← Business Application: Applications depend on technical capabilities
4. Technology Layer
Purpose: Provides the technical foundation and infrastructure for application deployment and operation.
Core Components
Architecture
- Definition: Architectural patterns and designs for system implementation
- Role: Design blueprint for technical implementation
- Relationships: "Designed using" and connected to deployment components
Component (Planned)
- Definition: Logical architectural components in design phase
- Role: Planned technical elements before deployment
- Relationship: "Delivers" technical capabilities
Component (Deployed)
- Definition: Physical implementation of planned components
- Role: Runtime technical elements
- Relationship: "Realized by" vendor products
Tech Capability
- Definition: Technical functions provided by deployed components
- Role: Foundational technical services
- Relationship: "Realized by" deployed components
Vendor Product
- Definition: Commercial or open-source products used in implementation
- Role: Actual technology products and tools
- Relationship: "Realizes" deployed components
System Architecture Detail
System of Systems
- Multi-layered architecture showing system composition
- Information System: Contains individual systems with interfaces and components
- System Components: API, Process, Application, Function layers
- Platform Layer: Foundational services and data management
- Infrastructure: Physical and virtual infrastructure components
External System
- Systems outside organizational boundary
- Integration points and external dependencies
Deployment Architecture
Deployment Environment
- Application Workload: Categorized by deployment type
- Deployed Software: Applications, Functions, External Systems
- Deployed Middleware: Platforms, Datastores
- Hardware: Infrastructure (Physical or Virtual)
- Management Tools: Operations, SMS Systems, OPS Tools
Runtime Model Categories:
- Serverless: Event-driven, scalable functions
- External Systems: Third-party integrations
- SaaS: Software-as-a-Service solutions
- Management and Monitoring Tools: Operational support systems
Model Relationships and Dependencies
Vertical Alignment
- Top-Down: Strategic objectives drive business design, which influences application selection and technology choices
- Bottom-Up: Technology capabilities enable application features, which support business processes and strategic goals
Horizontal Integration
- Within Strategy: Business objectives align with value streams
- Within Business: Processes, services, and offerings work together
- Within Application: Applications, capabilities, and data integrate seamlessly
- Within Technology: Components, products, and deployment models coordinate
Cross-Layer Dependencies
Strategy → Business
- Business objectives applied to value streams
- Value streams enabled by business capabilities
Business → Application
- Business capabilities applied to and provided by applications
- Business processes depend on technical capabilities
Application → Technology
- Applications designed using architectures
- Technical capabilities realized by deployed components
Using the Model
For Enterprise Architects
Portfolio Planning
- Start with Business Objectives in Strategy layer
- Map Value Streams and required Business Capabilities
- Identify supporting Business Applications and Data requirements
- Design appropriate Technology Architecture and Deployment models
Impact Analysis
- Trace relationships up and down the model to understand change impacts
- Use dependency mapping to identify affected components
- Assess alignment between strategy and implementation
For Solution Architects
System Design
- Reference Business Capabilities to understand requirements
- Design Application and Data architecture
- Select appropriate Technology Components and Vendor Products
- Plan Deployment architecture and Runtime models
Integration Planning
- Map External Systems and integration points
- Design Component interactions and dependencies
- Plan Tech Capability delivery through Vendor Products
For Technology Teams
Implementation Guidance
- Understand Business Application requirements
- Select appropriate Vendor Products and Tech Capabilities
- Design Deployment architecture with proper runtime models
- Implement Component architecture with required capabilities
Operations Planning
- Use Deployment model for operational planning
- Reference Management and Monitoring Tools requirements
- Plan Infrastructure (Physical or Virtual) capacity
Best Practices
Model Governance
- Consistency: Maintain consistent relationships across all layers
- Traceability: Ensure clear traceability from strategy to implementation
- Validation: Regularly validate model against actual implementation
Portfolio Management
- Alignment: Verify strategic alignment through the model layers
- Optimization: Identify optimization opportunities through dependency analysis
- Risk Management: Use model to assess impact of changes and risks
Architecture Development
- Iterative Design: Use model to iterate between business and technical design
- Reuse: Identify reusable components and capabilities across the model
- Standards: Establish consistent patterns and standards within each layer
Integration with AppFaktors Reports
The Portfolio Model directly supports the reporting capabilities:
- Technology Landscape Reports: Analyze Technology layer components and relationships
- Application Portfolio: Assess Application & Data layer health and alignment
- Capability Reports: Evaluate Business and Technical capability coverage
- Architecture Reports: Monitor Technology layer implementation and compliance
Conclusion
The AppFaktors Enterprise Architecture Portfolio Model provides a comprehensive framework for managing the complexity of enterprise architecture. By organizing artifacts across Strategy, Business, Application & Data, and Technology layers with clear relationships, organizations can maintain alignment between business objectives and technical implementation while enabling effective governance and portfolio management.